Types of EC2 Placement Groups
Upon launching new EC2 instances, the service tends to add the instance so that every one of your instances get spread out over underlying hardware in order to get the lowest possible correlated number of failures. Placement Groups are used for the sake of influencing the placement interdependent groups of instances so that they supply the requirements of your workload. According to which type of workload you possess; you may get to create a placement group through utilizing a chosen placement strategy out of the following ones:
- Cluster: works by packing instances close to each other in one Availability Zone. It allows for workloads to reach the low-latency network performance that is needed for the sake of achieving tightly-coupled node-to-node communication which is normal out of HPC apps.
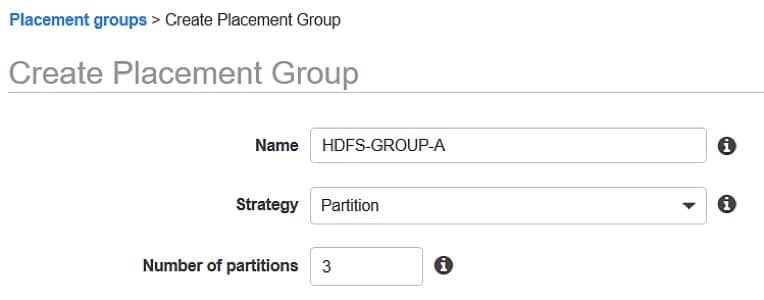
- Partition: sends instances over logical partitions in a way that enables groups of instances in one partition to not share the underlying hardware with other groups of instances that are found in differing partitions. It is utilized by enormous distributed and replicated workloads, like Cassandra, Hadoop or Kafka.
- Spread: places a small group of instances in a strict manner over unique underlying hardware in order to lessen correlated failures.
No fees are taken for the creation of placement groups.
AWS EC2 Cluster Placement Groups
EC2 Placement Groups – cluster placement groups
A logical grouping of instances in one Availability Zone.
Capable of spanning peered VPCs in the same Region.
Instances sharing this same group get a greater per-flow throughput limit of 10 Gbps for TCP/IP traffic + they get added to the network where there is exact high-bisection bandwidth segment.
The below picture highlights instances of a cluster placement group.
EC2 Placement Groups – cluster availability zone
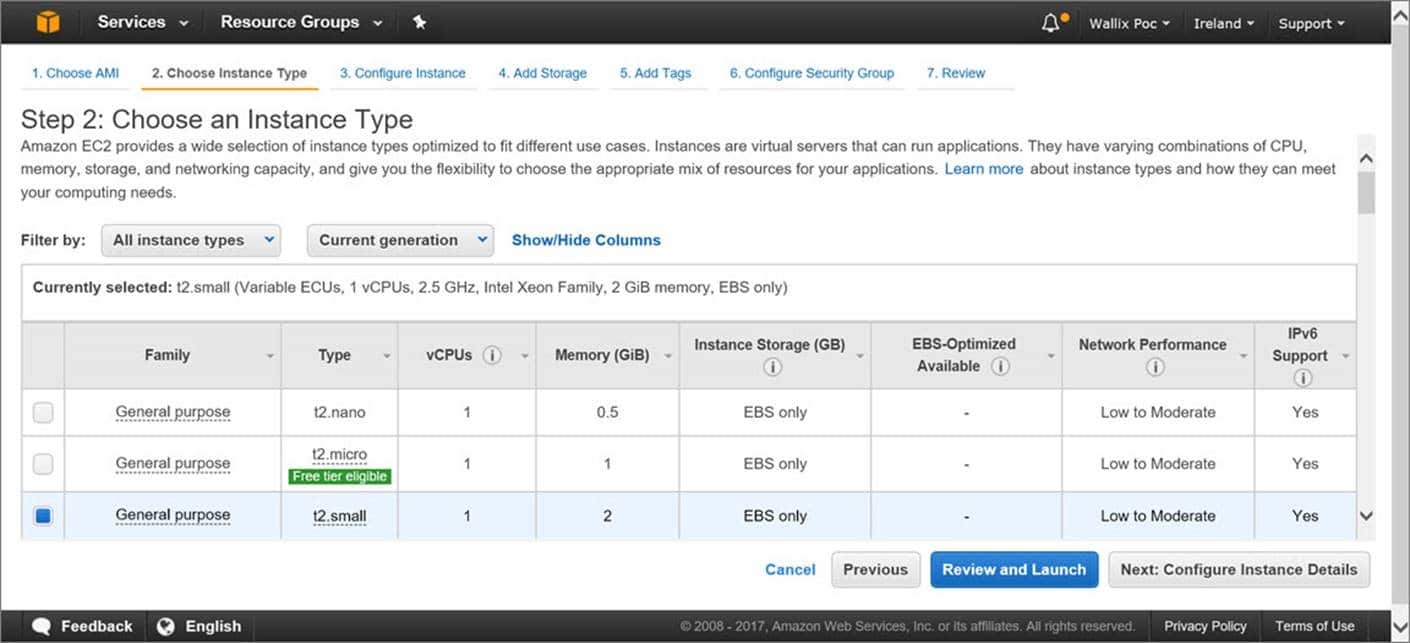
They are ideal for apps that work with both low network latency and high network throughput, or one of them. Also ideal for cases where the biggest part of the network traffic is spread between the instances. For offering the least latency and the greatest network performance for packet-per-second for your chosen placement group, select one instance type which works with enhanced networking.
It is best to launch an instance through this procedure:
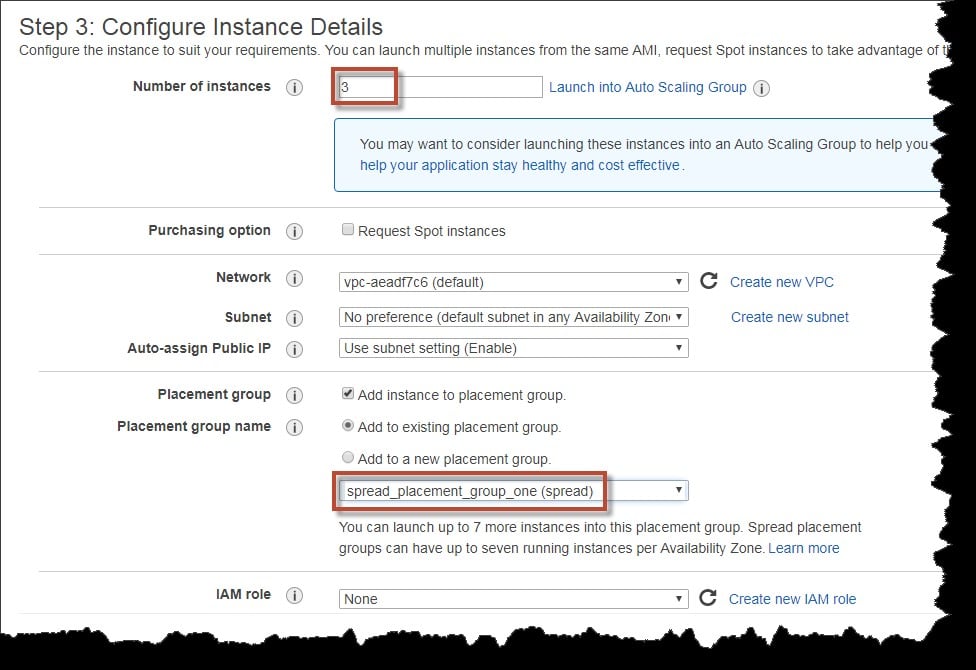
- Single launch request for the sake of launching as much instances as required in your chosen placement group.
- Exact instance type for every instance found in your chosen placement group.
In case after a while you decide to add even more instances into your placement group, or in case you choose to start launching multiple instance types in your chosen placement group, you are going to have to raise your possibility of acquiring an error of insufficient capacity.
In case of you stop one instance from your chosen placement group and later want to start it once again, it will keep on running in your chosen placement group. Yet, this start will fail in the case that there wasn’t enough possible capacity for this instance.
In case of receiving an error for capacity upon the launching of an instance found in your placement group that contains instances which are already running, you will have to stop and start every single one of your instances that are located in this placement group, and then go ahead with performing the launch again. The start of instances might actually send them to hardware which possesses capacity for every one of your requested instances.
AWS EC2 Partition Placement Groups
EC2 Placement Groups – partition placement groups
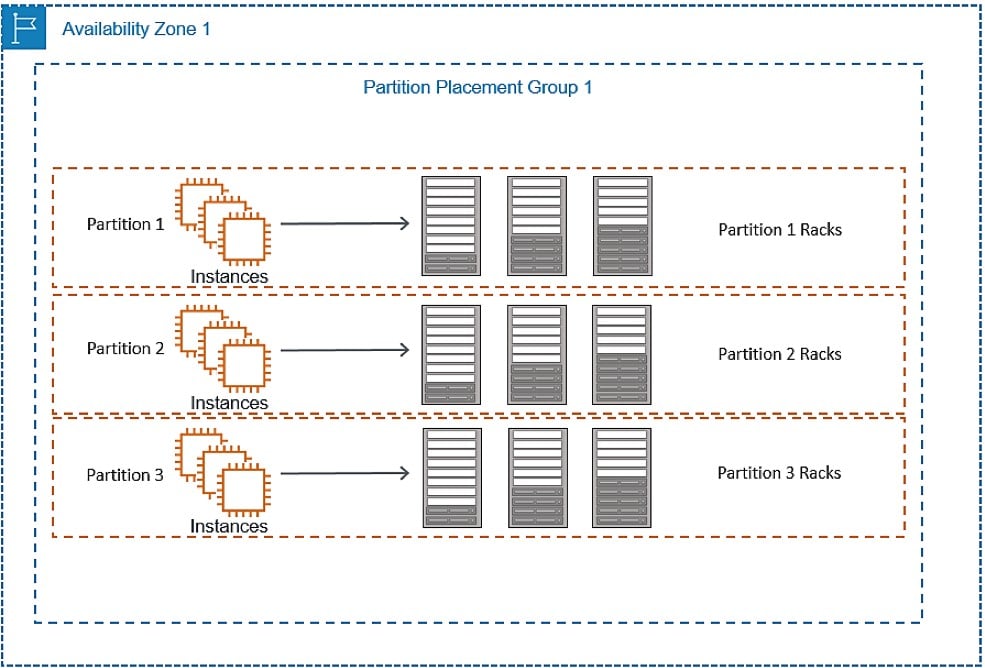
These placement groups help reduce the likelihood of correlated hardware failures for your application. With partition placement groups, EC2 will tend to divide every group into logical segments [partitions]. EC2 makes sure that every one of these partitions falls into a placement group which maintains its very own set of racks. Every rack includes its unique network + power source. There cannot be any 2 partitions found in the same placement group while sharing the exact racks, making you capable of isolating the effect of hardware failure within your application.
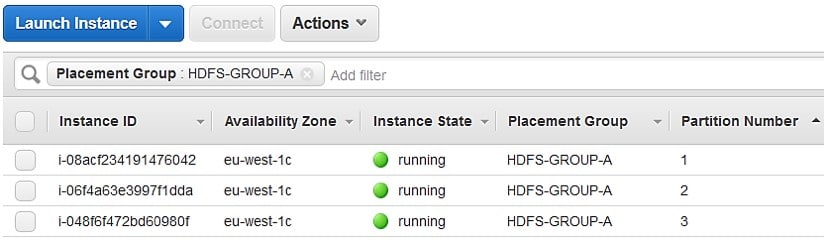
The below picture shows a partition placement group located in the same Availability Zone. It presents instances being placed in one partition placement group that contains 3 partitions: Partition 1 – Partition 2 – Partition 3. Every one of the partitions has a number of instances. Instances in one partition are not able to share racks with instances of other partitions, making it possible for you to hold the effect of just one hardware failure merely to the associated partition.
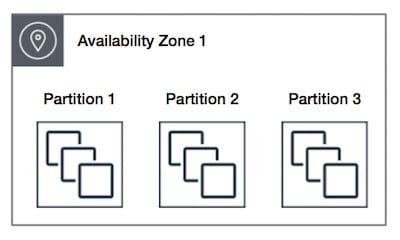
EC2 Placement Groups – partition availability zone
– Deploys huge distributed and replicated workloads, like: HBase, Cassandra and HDFS, over unique racks.
– Distributes the instances in an even manner over a number of partitions specified by you.
– Take more control over the place where instances get placed.
A partition placement group:
– Partitions in various Availability Zones found in one same Region.
– Seven partitions per Availability Zone as a maximum.
– Possible number of instances launched into a partition placement group: merely limited by the limits of the user’s account.
– Offer visibility into the partitions to check the instances’ placement in partitions.
– Sharing data with topology-aware applications, like: Cassandra, HBase and HDFS. Such apps take this data in order to perform some intelligent data replication decisions for the sake of raising data to become more available and durable.
In case there was insufficient unique hardware to take on your launching request, this request will end in failure. Yet, extra distinct hardware will become available as time goes by, hence it is possible for you retry your request at another time.
AWS EC2 Spread Placement Groups

AWS EC2 Placement Groups – spread placement groups
It’s a group of instances which get placed on different racks, possessing their very own unique network + power source.
The below picture illustrates seven instances in one same Availability Zone where they are placed with a spread placement group. Each instance is placed on differing racks.
These groups are perfect for apps containing a small number of critical instances which need to stay separated one another. Launching instances in a spread placement group instances launched will minimize the danger of continuously occurring failures which can happen as instances tend to share the exact same racks.
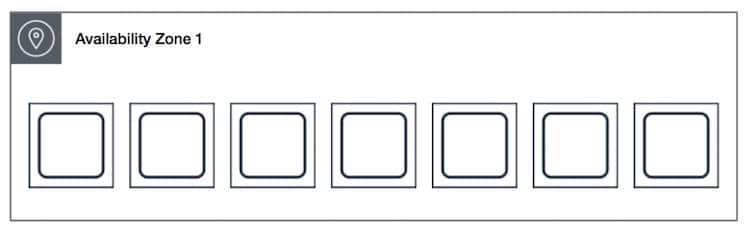
AWS EC2 Placement Groups – spread availability zone 1
Spread placement groups:
– Offer access to unique racks
– Perfect for the sake of mixing instance types or tending to launch instances as time goes by
– Possible to span various Availability Zones in the exact Region
– Maximum number of 7 running instances for every Availability Zone of a group.
In case in a spread placement group there was insufficient unique hardware to take on your launching request, this request will end in failure. Yet, extra distinct hardware will become available as time goes by, hence it is possible for you retry your request at another time.