AWS RDS Instance Types
About Amazon RDS instance types:

AWS RDS Instance Types – AWS RDS Instance Type Selection
– There is a vast choice of instance types that are perfectly optimized to take on various relational database use cases
– Instance types are composed of different combinations of CPU, storage, memory and networking capacity and provide you with the freedom to select the perfect mixture of resources for a specific database
– Every instance type contains various instance sizes, which will give you the ability to scale your database so that it matches the needs of your required workload
– Not all the instance types are going to be supported for each and every database version, engine, region or edition.
General Purpose Instance Types
AWS RDS Instance Types – General Purpose Instance Types
- T3
- T2
- M5
- M4
Memory Optimized Instance Types
- R5
- R4
- X1e
- X1
- Z1d
Features of AWS RDS Instances:
AWS RDS Instance Types – AWS RDS Change Instance Type
The RDS database instances offer you various extra features that can help you in deploying, managing, and even scaling database workloads.
Offering Database Storage Options for AWS RDS
The storage, which is set for RDS for the following databases: MariaDB, MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server and Oracle will be built on a strong and maintainable storage service called the Amazon EBS.
There are 3 types of volume that are offered by RDS for the sake of achieving the requirements of specific database workloads, and they are the following: Provisioned IOPS (SSD), Magnetic, and General Purpose (SSD).
Provisioned IOPS (SSD): They provide storage along with low latency and stable performance, and they are specifically built for I/O intensive database workloads.
Magnetic: They offer a low price for every gigabyte and they are offered compatibility that is backward.
General Purpose (SSD): It is a general purpose, SSD-backed type of volume which is best selected by default for a wide variety of workloads.
Aurora sheds light on a storage system that tolerates faults while being distributed and works as a self-healing system that is capable of automatically scaling to a maximum of 64 TB for every database instance. It offers great availability and performance, reaching up to 15 low-latency read replicas, a recovery that is point-in-time, constant backup to S3, and replication over 3 AZs.
Offering Burstable Performance Instances

AWS RDS Instance Types – AWS RDS Burstable Performance Instances
RDS gives you the ability to select either Fixed Performance Instances, such as R5 and M5 or Burstable Performance Instances, like T3.
Burstable Performance Instances offer their users a CPU performance at the baseline level and the capability of bursting beyond this baseline.
RDS T3 instances are capable of maintaining great CPU performance for the amount of time that a workload requires. For a lot of the general-purpose workloads, T3 instances are going to offer sufficient performance with no need for extra costs.
The hourly T3 instance cost will automatically cover every single provisional spike in usage when the average CPU utilization of a T3 instance reaches the baseline over a twenty-four-hour window.
CPU Credits take control of T3 instances’ baseline performance and capability of bursting. Every single T3 instance constantly gets CPU Credits, with a rate depending on instance size. T3 instances accumulate CPU Credits upon being idle and utilize CPU credits that are active. Every CPU Credit is capable of offering a complete CPU core performance for a period of 1 minute.
A lot of database workloads do not actually require constantly great levels of CPU but greatly take advantage of gaining total access over fully swift CPUs whenever they are required.
Burstable Performance instances are specifically built for the previously mentioned use cases. In case you require constant great CPU performance for databases, it is better for you to utilize Fixed Performance Instances.
Offering Enhanced Networking
This feature enables users to obtain greatly higher PPS performance, lesser network jitter as well as lesser latencies. It utilizes a newly designed network virtualization stack which offers greater I/O performance along with lesser CPU utilization in comparison with normal implementations.
RDS will directly enable Enhanced Networking for specific database instance types that are supported.
Offering EBS-optimized Instances
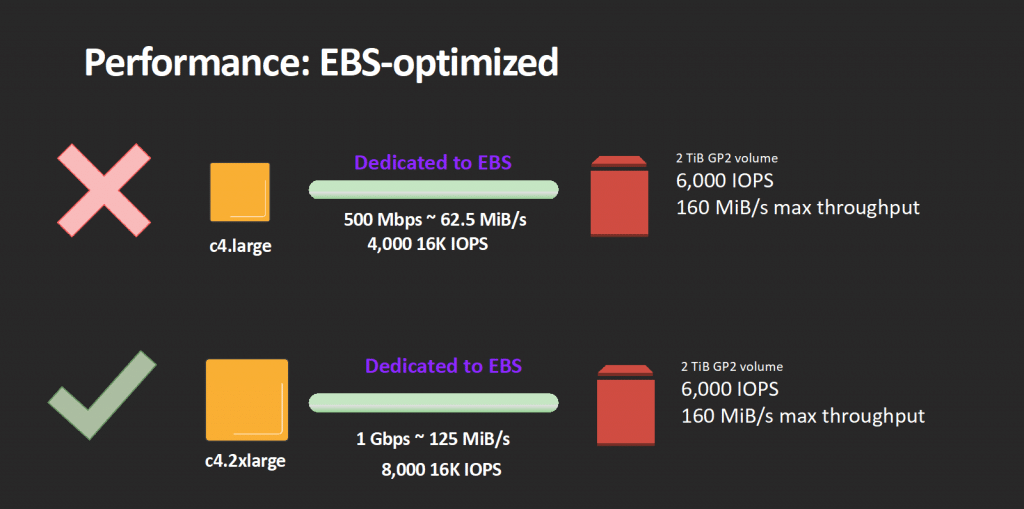
AWS RDS Instance Types – AWS RDS EBS-Optimized Instances
Those instances allow RDS to completely utilize the IOPS provisioned on an EBS volume.
Dedicated throughput is delivered by EBS-optimized instances between RDS and EBS, with options starting with 500 all the way to 4,000 Mbps, according to which instance type is being utilized.
They are developed for the sake of being utilized along with either Provisioned or Standard IOPS Amazon EBS volumes.
The dedicated throughput lessens contention happening between EBS I/O and different coming traffic from the chosen RDS instance while offering optimal performance for selected EBS volumes.
It’s better to utilize Provisioned IOPS volumes with EBS-optimized instances as well as with instances that are capable of supporting cluster networking for apps having great storage I/O requirements.
Upon attaching to EBS-optimized instances, Provisioned IOPS volumes are capable of achieving single-digit millisecond latencies and they are developed for the sake of delivering within ten percent of provisioned IOPS performance almost at all times.
See Also