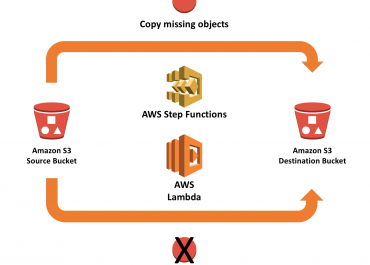
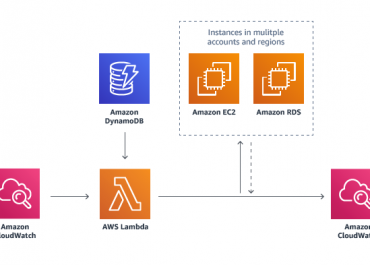
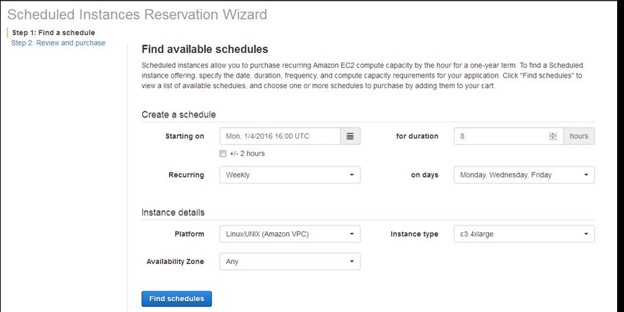
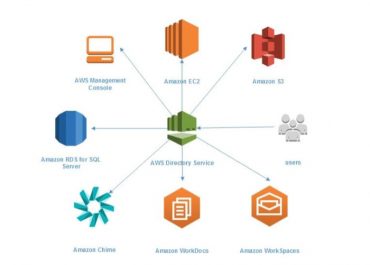
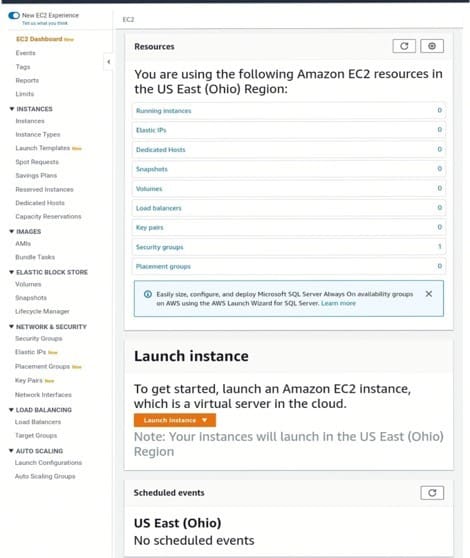
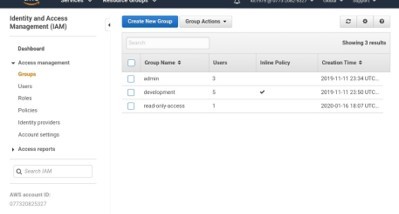
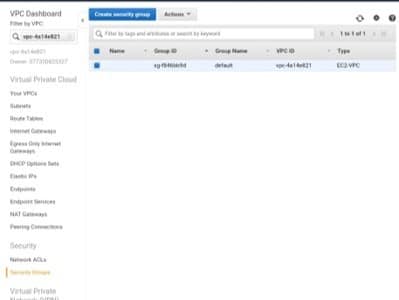
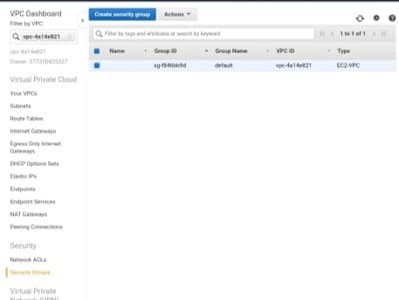
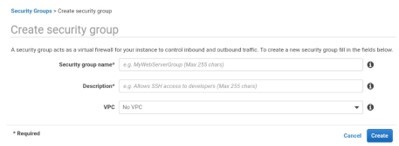
VPC
1. Write,
Read,
Delete,
For objects from one byte to five terabytes of data,
Number of objects to store is unlimited.
2. Objects are stored in a bucket and retrieved using a special key assigned by the developer.
3. Objects that are stored in a specific Region, remain there until transferred.
4. Authentication mechanisms to make sure that data is secure from unauthorized access. Objects may be private or public, and specific users can get rights granted.
5. Standards-based REST and SOAP interfaces are created for running with various Internet-development toolkits.
6. Flexibility so that protocol or functional layers may easily be added.
Default download protocol: HTTP, and S3 API supports: HTTPS as well.
Default connections are HTTPS for AWS CLI and SDK.
7. Functionality for simplifying manageability of data through lifetime.
Options to:
-Segregate data by buckets
-Monitor and control spend
-Archive data to lower cost storage options
See Also
9. Easy management
Very easy to manage.
Store Management feature allows for a data-driven approach for:
-Storing optimization
-Data security
-Management efficiency
- Minimal feature set:
VPC
1. Write,
Read,
Delete,
For objects from one byte to five terabytes of data,
Number of objects to store is unlimited.
2. Objects are stored in a bucket and retrieved using a special key assigned by the developer.
3. Objects that are stored in a specific Region, remain there until transferred.
4. Authentication mechanisms to make sure that data is secure from unauthorized access. Objects may be private or public, and specific users can get rights granted.
5. Standards-based REST and SOAP interfaces are created for running with various Internet-development toolkits.
6. Flexibility so that protocol or functional layers may easily be added.
Default download protocol: HTTP, and S3 API supports: HTTPS as well.
Default connections are HTTPS for AWS CLI and SDK.
7. Functionality for simplifying manageability of data through lifetime.
Options to:
-Segregate data by buckets
-Monitor and control spend
-Archive data to lower cost storage options
See Also
Route 53
Deeply integrated with other AWS services.
Easy to build solutions that use a variety of AWS services.
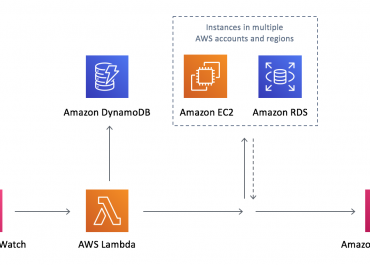
Integrations include:
Storage Gateway
CloudFront
CloudWatch
Kinesis
RDS
Glacier
EBS
DynamoDB
Redshift
Route 53
EMR
VPC
KMS
Lambda
9. Easy management
Very easy to manage.
Store Management feature allows for a data-driven approach for:
-Storing optimization
-Data security
-Management efficiency
- Minimal feature set:

VPC
1. Write,
Read,
Delete,
For objects from one byte to five terabytes of data,
Number of objects to store is unlimited.
2. Objects are stored in a bucket and retrieved using a special key assigned by the developer.
3. Objects that are stored in a specific Region, remain there until transferred.
4. Authentication mechanisms to make sure that data is secure from unauthorized access. Objects may be private or public, and specific users can get rights granted.
5. Standards-based REST and SOAP interfaces are created for running with various Internet-development toolkits.
6. Flexibility so that protocol or functional layers may easily be added.
Default download protocol: HTTP, and S3 API supports: HTTPS as well.
Default connections are HTTPS for AWS CLI and SDK.
7. Functionality for simplifying manageability of data through lifetime.
Options to:
-Segregate data by buckets
-Monitor and control spend
-Archive data to lower cost storage options
See Also
Amazon S3 Service Features
Amazon S3 makes it profoundly easy and simple to move large data either on or out. This is possible with the help of Amazon’s cloud data migration options. Once data is stored in S3, it can directly get tired into low cost and longer-term cloud storage classes as S3 Standard.
What are the Features of Amazon S3 Services?
1. Simplicity
It is very simple to use.
Has a web-based management console and a mobile application.
Can be integrated with third-party technologies like full REST APIs and SDKs.
2. Durability
Provides a durability of 99.99999% of objects.
Allows for durable infrastructure to store extremely important data.
Data is redundantly stored across multiple facilities and multiple devices.
3. Scalability
Allows storing as much data as needed.
Access this data whenever required.
Scale up or scale down storage needs whenever necessary.
4. Security
No security problems.
Data transferred over SSL.
Automatic encryption of data when uploaded.
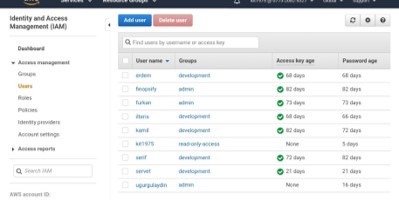
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) to grant object permissions and control access all data.
5. Availability
Offers 99.99% availability of objects yearly.
Backed by Amazon S3 Service Level Agreement, which ensures that you rely on it whenever necessary.
6. Low Costing
Allows storing huge amounts of data with very low cost.
Data can be migrated to S3 standard infrequent access or to Amazon Glacier which further reduces cost.
7. Simple data transferring
Easy to move large data in or out.
Extremely cost-effective.
To import or export from S3, choose from:
-Network optimized
-Physical disk-based
-Third-party connector methods
8. Integration
Route 53
Deeply integrated with other AWS services.
Easy to build solutions that use a variety of AWS services.
Integrations include:
Storage Gateway
CloudFront
CloudWatch
Kinesis
RDS
Glacier
EBS
DynamoDB
Redshift
Route 53
EMR
VPC
KMS
Lambda
9. Easy management
Very easy to manage.
Store Management feature allows for a data-driven approach for:
-Storing optimization
-Data security
-Management efficiency
- Minimal feature set:

VPC
1. Write,
Read,
Delete,
For objects from one byte to five terabytes of data,
Number of objects to store is unlimited.
2. Objects are stored in a bucket and retrieved using a special key assigned by the developer.
3. Objects that are stored in a specific Region, remain there until transferred.
4. Authentication mechanisms to make sure that data is secure from unauthorized access. Objects may be private or public, and specific users can get rights granted.
5. Standards-based REST and SOAP interfaces are created for running with various Internet-development toolkits.
6. Flexibility so that protocol or functional layers may easily be added.
Default download protocol: HTTP, and S3 API supports: HTTPS as well.
Default connections are HTTPS for AWS CLI and SDK.
7. Functionality for simplifying manageability of data through lifetime.
Options to:
-Segregate data by buckets
-Monitor and control spend
-Archive data to lower cost storage options
See Also